|

People with vitiligo
may have eye abnormalities and also have a higher incidence of thyroid
disease, diabetes mellitus, and pernicious anemia. Vitiligo affects about
1-2% of the world's population. It is more easily observed in sun-exposed
areas of the body and in darker skin types, but it affects any area of
the body and all races.
Vitiligo seems
to affect men and women equally, although women more frequently seek treatment
for the disorder.
|
 |
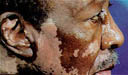
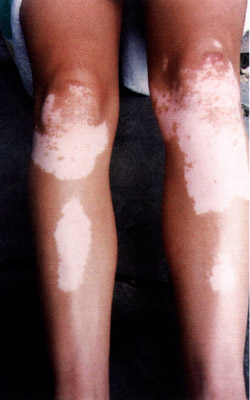
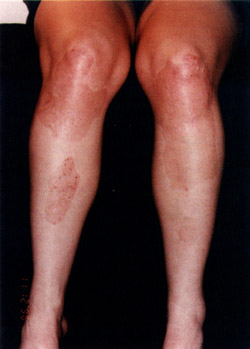
Vitiligo may appear
as one or two well-defined white patches or it may appear over large portions
of the body. Typical sites for generalized vitiligo are areas surrounding
body openings, bony areas, fingers, and toes. It can begin at any age
but about 50% of the time it starts before the age of 20.
Though the pigment-making
cells of the skin, or melanocytes, are structually intact, hey have lost
the ability to synthesize the pigment. The reason for the condition is
unclear. Individuals with vitiligo are usually in good general healthy,
but vitiligo presents a cosmetic problem that can be serious in dark-skinned
individuals. Vitiligo is also known as leukoderma.
|
 |
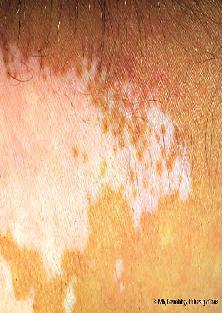
Vitiligo is a disorder
with complex causes. People with vitiligo seem to inherit a genetic predisposition
for the disorder, and the appearance of disorder can be brought on by
a variety of precipitating causes. Many people report that their vitiligo
first appeared following a traumatic or stressful event, such as an accident,
job loss, and death of a family member, severe sunburn, or serious illness.
There are at least three theories about the underlying mechanism of vitiligo.
|
 |
One theory says
nerve endings in the skin release a chemical that is toxic to the melanocytes.
A second theory
states that the melanocytes simply self-destruct. The third explanation
is that vitiligo is a type of autoimmune disease in which the immune system
targets the body's own cells and tissues.
The primary symptom
of vitiligo is the loss of skin color. Hair growing from the affected
skin areas also lacks color. In addition, people with vitiligo may have
pigment abnormalities of the retina or iris of the eyes. A minority of
patients also may have inflammation of the retina or iris, but vision
is not usually impaired.
|
| The
diagnosis of vitiligo is usually made by observation. Progressive, white
areas found at typical sites point to a diagnosis of vitiligo. If the diagnosis
is not certain, the doctor will test for other conditions that can mimic
vitiligo, such as chemical leukoderma or systemic lupus erythematosus. If
the tests rule out other conditions, vitiligo is confirmed. |
 |
|
 |
An aromatic so
called Atamanta plant. Indeed it has a miracle effect for curing the white
vitilgo. It has always worked with the affected people. It works with
a little exposure of the effected skin into the sun.
Many Vitiligo patients
have successfully used this Arabic plant extracted medication taken with
honey. Vitiligo is characterized by skin depigmentation and is commonly
associated with the immune system.
This Herb can help
regulate the immune system by bringing it to its healthiest, strongest,
balanced levels. Repigmentation results can be seen within the first week
of taking this product.
Vitiligo can be
cured permanently with this Atamanta plant.
|
 |
|